MySQL查询语句
语法:select [选项] 列名 [from 表名] [where 条件] [group by 分组] [order by 排序][having 条件] [limit 限制]
字段表达式
mysql> select '锄禾日当午';
+------------+
| 锄禾日当午 |
+------------+
| 锄禾日当午 |
+------------+
mysql> select 10*10;
+-------+
| 10*10 |
+-------+
| 100 |
+-------+
通过as给字段取别名
mysql> select '锄禾日当午' as content;
+------------+
| content |
+------------+
| 锄禾日当午 |
+------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select 10*10 as result;
+--------+
| result |
+--------+
| 100 |
+--------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
多学一招:as可以省略
mysql> select 10*10 result;
+--------+
| result |
+--------+
| 100 |
+--------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
from子句
from:来自,from后面跟的是数据源。数据源可以有多个。返回笛卡尔积。
插入测试表
mysql> create table t1(
-> id int,
-> name varchar(10)
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.05 sec)
mysql> create table t2(
-> field1 varchar(10),
-> field2 varchar(10)
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> insert into t1 values (1,'tom'),(2,'berry');
Query OK, 2 rows affected (0.00 sec)
Records: 2 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> insert into t2 values ('333','333'),('444','444');
Query OK, 2 rows affected (0.02 sec)
Records: 2 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
测试多个数据源
mysql> select * from t1,t2; # 返回笛卡尔积
+------+-------+--------+--------+
| id | name | field1 | field2 |
+------+-------+--------+--------+
| 1 | tom | 333 | 333 |
| 2 | berry | 333 | 333 |
| 1 | tom | 444 | 444 |
| 2 | berry | 444 | 444 |
+------+-------+--------+--------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
dual表
dual表是一个伪表。在有些特定情况下,没有具体的表的参与,但是为了保证select语句的完整又必须要一个表名,这时候就使用伪表。
mysql> select 10*10 as result from dual; #dual表是用来保证select语句的完整性。
+--------+
| result |
+--------+
| 100 |
+--------+
where子句
where后面跟的是条件,在数据源中进行筛选。返回条件为真记录
MySQL支持的运算符
>大于<小于>=<==!=- and 与
- or 或
- not 非
mysql> select * from stu where stusex='男'; # 查找性别是男的记录
mysql> select * from stu where stuage>=20; # 查找年龄不低于20的记录
思考:如下代码输出什么
select * from stu where 1 # 返回所有数据库
select * from stu where 0 #返回空记录
思考:如何查找北京和上海的学生
mysql> select * from stu where stuaddress='上海' or stuaddress='北京';
+--------+---------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
| stuNo | stuName | stuSex | stuAge | stuSeat | stuAddress | ch | math |
+--------+---------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
| s25301 | 张秋丽 | 男 | 18 | 1 | 北京 | 80 | NULL |
| s25302 | 李文才 | 男 | 31 | 3 | 上海 | 77 | 76 |
| s25303 | 李斯文 | 女 | 22 | 2 | 北京 | 55 | 82 |
| s25320 | Tom | 男 | 24 | 8 | 北京 | 65 | 67 |
+--------+---------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
in | not in
上面的查询上海和北京的学生的SQL可以通过in语句来实现
mysql> select * from stu where stuaddress in ('北京','上海');
练习:
1、查找学号是s25301,s25302,s25303的学生
mysql> select * from stu where stuno in ('s25301','s25302','s25303');
2、查找年龄是18,19,20的学生
mysql> select * from stu where stuage in(18,19,20);
3、查找不是北京和上海的学生
mysql> select * from stu where stuaddress not in ('北京','上海');
between…and|not between…and
查找某个范围的记录
1、查找年龄在18~20之间的学生
mysql> select * from stu where stuage>=18 and stuage<=20; # 方法一
mysql> select * from stu where stuage between 18 and 20; # 方法二
2、查找年龄不在18~20之间的学生
mysql> select * from stu where stuage<18 or stuage>20; #方法一
mysql> select * from stu where not (stuage>=18 and stuage<=20);
mysql> select * from stu where stuage not between 18 and 20;
is null | is not null
脚下留心:查询一个为空的字段不能用等于,必须用is null
查找缺考的学生
mysql> select * from stu where ch is null or math is null; # 查找缺考的人
+--------+----------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
| stuNo | stuName | stuSex | stuAge | stuSeat | stuAddress | ch | math |
+--------+----------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
| s25301 | 张秋丽 | 男 | 18 | 1 | 北京 | 80 | NULL |
| s25304 | 欧阳俊雄 | 男 | 28 | 4 | 天津 | NULL | 74 |
+--------+----------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
查找参加考试的学生
mysql> select * from stu where ch is not null and math is not null;
聚合函数
sum() 求和
avg() 求平均值
max() 求最大值
min() 求最小值
count() 求记录数
#求语文总分、语文平均分、语文最高分、语文最低分、总人数
mysql> select sum(ch) '语文总分',avg(ch) '语文平均分', max(ch) '语文最高分',min(ch) '语文最低分',count(*) '总人数' from stu;
+----------+------------+------------+------------+--------+
| 语文总分 | 语文平均分 | 语文最高分 | 语文最低分 | 总人数 |
+----------+------------+------------+------------+--------+
| 597 | 74.6250 | 88 | 55 | 9 |
+----------+------------+------------+------------+--------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
通配符
_ [下划线] 表示任意一个字符
% 表示任意字符
练习
1、满足“T_m”的有(A、C)
A:Tom B:Toom C:Tam D:Tm E:Tmo
2、满足“Tm”的有(B、C )
A:Tmom B:Tmmm C:T1m2 D:Tmm E:Tm
3、满足“张%”的是(A、B、C、D)
A:张三 B:张三丰 C:张牙舞爪 D:张 E:小张
4、满足“%诺基亚%”的是(A、B、C、D)
A:诺基亚2100 B:2100诺基亚 C:把我的诺基亚拿过来 D:诺基亚
模糊查询(like)
# 查找姓张的同学
mysql> select * from stu where stuname like '张%';
+--------+---------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
| stuNo | stuName | stuSex | stuAge | stuSeat | stuAddress | ch | math |
+--------+---------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
| s25301 | 张秋丽 | 男 | 18 | 1 | 北京 | 80 | NULL |
+--------+---------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
#例题
mysql> select * from stu where stuname like 'T_m';
+--------+---------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
| stuNo | stuName | stuSex | stuAge | stuSeat | stuAddress | ch | math |
+--------+---------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
| s25320 | Tom | 男 | 24 | 8 | 北京 | 65 | 67 |
+--------+---------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
1.6.11 order by排序
asc:升序【默认】
desc:降序
mysql> select * from stu order by ch desc; # 语文成绩降序排列
mysql> select * from stu order by math asc; # 数学成绩升序排列
mysql> select * from stu order by math; # 默认升序排列
多列排序
#年龄升序,成绩降序
mysql> select *,(ch+math) as '总分' from stu order by stuage asc,(ch+math) desc;
思考如下代码表示什么含义
select * from stu order by stuage desc,ch desc; #年龄降序,语文降序
select * from stu order by stuage desc,ch asc; #年龄降序,语文升序
select * from stu order by stuage,ch desc; #年龄升序、语文降序
select * from stu order by stuage,ch; #年龄升序、语文升序
group by[分组查询]
将查询的结果分组,分组查询目的在于统计数据。
# 按性别分组,显示每组的平均年龄
mysql> select avg(stuage) as '年龄',stusex from stu group by stusex;
+---------+--------+
| 年龄 | stusex |
+---------+--------+
| 22.7500 | 女 |
| 25.4000 | 男 |
+---------+--------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
# 按地区分组,每个地区的平均年龄
mysql> select avg(stuage) as '年龄',stuaddress from stu group by stuaddress;
+---------+------------+
| 年龄 | stuaddress |
+---------+------------+
| 31.0000 | 上海 |
| 21.3333 | 北京 |
| 27.0000 | 天津 |
| 23.0000 | 河北 |
| 23.0000 | 河南 |
+---------+------------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
脚下留心:
1、如果是分组查询,查询字段必须是分组字段和聚合函数。
2、查询字段是普通字段,只取第一个值
通过group_concat()函数将同一组的值连接起来显示
mysql> select group_concat(stuname),stusex from stu group by stusex;
+-------------------------------------+--------+
| group_concat(stuname) | stusex |
+-------------------------------------+--------+
| 李斯文,诸葛丽丽,梅超风,Tabm | 女 |
| 张秋丽,李文才,欧阳俊雄,争青小子,Tom | 男 |
+-------------------------------------+--------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
多学一招:【了解】
1、分组后的结果默认会按升序排列显示
2、也是可以使用desc实现分组后的降序
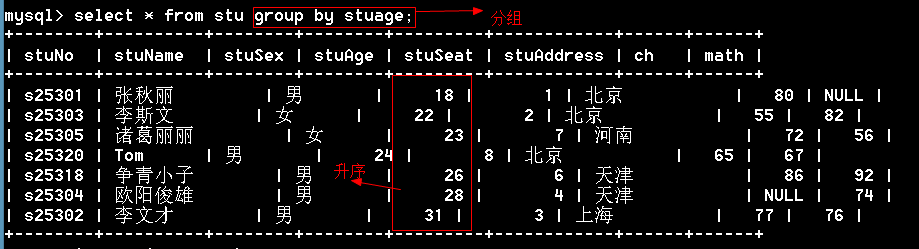
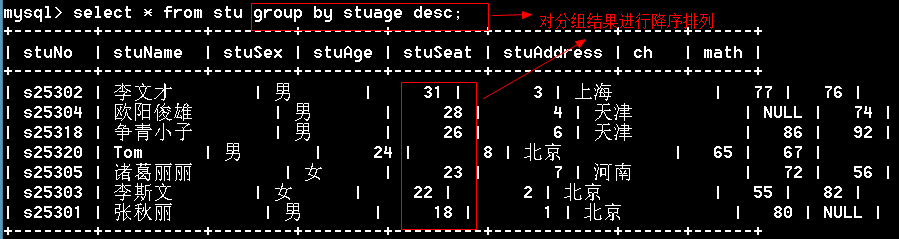
多列分组
mysql> select stuaddress,stusex,avg(stuage) from stu group by stuaddress,stusex;
+------------+--------+-------------+
| stuaddress | stusex | avg(stuage) |
+------------+--------+-------------+
| 上海 | 男 | 31.0000 |
| 北京 | 女 | 22.0000 |
| 北京 | 男 | 21.0000 |
| 天津 | 男 | 27.0000 |
| 河北 | 女 | 23.0000 |
| 河南 | 女 | 23.0000 |
+------------+--------+-------------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)
having条件
思考:数据库中的表是一个二维表,返回的结果是一张二维表,既然能在数据库的二维表中进行查询,能否在结果集的二维表上继续进行查询?
答:可以,having条件就是在结果集上继续进行筛选。
例题
mysql> select * from stu where stusex='男'; # 从数据库中查找
+--------+----------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
| stuNo | stuName | stuSex | stuAge | stuSeat | stuAddress | ch | math |
+--------+----------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
| s25301 | 张秋丽 | 男 | 18 | 1 | 北京 | 80 | NULL |
| s25302 | 李文才 | 男 | 31 | 3 | 上海 | 77 | 76 |
| s25304 | 欧阳俊雄 | 男 | 28 | 4 | 天津 | NULL | 74 |
| s25318 | 争青小子 | 男 | 26 | 6 | 天津 | 86 | 92 |
| s25320 | Tom | 男 | 24 | 8 | 北京 | 65 | 67 |
+--------+----------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from stu having stusex='男'; # 从结果集中查找
+--------+----------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
| stuNo | stuName | stuSex | stuAge | stuSeat | stuAddress | ch | math |
+--------+----------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
| s25301 | 张秋丽 | 男 | 18 | 1 | 北京 | 80 | NULL |
| s25302 | 李文才 | 男 | 31 | 3 | 上海 | 77 | 76 |
| s25304 | 欧阳俊雄 | 男 | 28 | 4 | 天津 | NULL | 74 |
| s25318 | 争青小子 | 男 | 26 | 6 | 天津 | 86 | 92 |
| s25320 | Tom | 男 | 24 | 8 | 北京 | 65 | 67 |
+--------+----------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
思考如下语句是否正确
having和where的区别:
where是对原始数据进行筛选,having是对记录集进行筛选。
limit
语法:limit 起始位置,显示长度
mysql> select * from stu limit 0,2; # 从0的位置开始,取两条数据
+--------+---------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
| stuNo | stuName | stuSex | stuAge | stuSeat | stuAddress | ch | math |
+--------+---------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
| s25301 | 张秋丽 | 男 | 18 | 1 | 北京 | 80 | NULL |
| s25302 | 李文才 | 男 | 31 | 3 | 上海 | 77 | 76 |
+--------+---------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from stu limit 2,2; # 从2的位置开始,取两条数据
+--------+----------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
| stuNo | stuName | stuSex | stuAge | stuSeat | stuAddress | ch | math |
+--------+----------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
| s25303 | 李斯文 | 女 | 22 | 2 | 北京 | 55 | 82 |
| s25304 | 欧阳俊雄 | 男 | 28 | 4 | 天津 | NULL | 74 |
+--------+----------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
起始位置可以省略,默认是从0开始
mysql> select * from stu limit 2;
+--------+---------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
| stuNo | stuName | stuSex | stuAge | stuSeat | stuAddress | ch | math |
+--------+---------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
| s25301 | 张秋丽 | 男 | 18 | 1 | 北京 | 80 | NULL |
| s25302 | 李文才 | 男 | 31 | 3 | 上海 | 77 | 76 |
+--------+---------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
例题:找出班级总分前三名
mysql> select *,(ch+math) total from stu order by total desc limit 0,3;
+--------+----------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+-------+
| stuNo | stuName | stuSex | stuAge | stuSeat | stuAddress | ch | math | total |
+--------+----------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+-------+
| s25318 | 争青小子 | 男 | 26 | 6 | 天津 | 86 | 92 | 178 |
| s25321 | Tabm | 女 | 23 | 9 | 河北 | 88 | 77 | 165 |
| s25302 | 李文才 | 男 | 31 | 3 | 上海 | 77 | 76 | 153 |
+--------+----------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+-------+
多学一招:limit在update和delete语句中也是可以使用的。
查询语句中的选项
查询语句中的选项有两个:
1、 all:显示所有数据 【默认】
2、 distinct:去除结果集中重复的数据
mysql> select distinct stuaddress from stu;
+------------+
| stuaddress |
+------------+
| 上海 |
| 天津 |
| 河南 |
| 河北 |
| 北京 |
+------------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
union(联合)
插入测试数据
mysql> create table GO1(
-> id int primary key,
-> name varchar(20));
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.06 sec)
mysql> insert into Go1 values (1,'李白'),(2,'张秋丽');
Query OK, 2 rows affected (0.02 sec)
Records: 2 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
union的使用
作用:将多个select语句结果集纵向联合起来
语法:select 语句 union [选项] select 语句 union [选项] select 语句
mysql> select stuno,stuname from stu union select id,name from Go1;
+--------+----------+
| stuno | stuname |
+--------+----------+
| s25301 | 张秋丽 |
| s25302 | 李文才 |
| s25303 | 李斯文 |
| s25304 | 欧阳俊雄 |
| s25305 | 诸葛丽丽 |
| s25318 | 争青小子 |
| s25319 | 梅超风 |
| s25320 | Tom |
| s25321 | Tabm |
| 1 | 李白 |
| 2 | 张秋丽 |
+--------+----------+
例题:查询上海的男生和北京的女生
mysql> select stuname,stuaddress,stusex from stu where (stuaddress='上海' and stusex='男') or (stuaddress='北京' and stusex='女');
+---------+------------+--------+
| stuname | stuaddress | stusex |
+---------+------------+--------+
| 张秋丽 | 上海 | 男 |
| 梅超风 | 北京 | 女 |
+---------+------------+--------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select stuname,stuaddress,stusex from stu where stuaddress='上海' and stusex='男' union select stuname,stuaddress,stusex from stu where stuaddress='北京' and stusex='女';
+---------+------------+--------+
| stuname | stuaddress | stusex |
+---------+------------+--------+
| 张秋丽 | 上海 | 男 |
| 梅超风 | 北京 | 女 |
+---------+------------+--------+
2 rows in set (0.02 sec)
union的选项
union的选项有两个
1、 all:显示所有数据
2、 distinct:去除重复的数据【默认】
mysql> select name from go1 union select stuname from stu;
+----------+
| name |
+----------+
| 李白 |
| 张秋丽 |
| 李文才 |
| 李斯文 |
| 欧阳俊雄 |
| 诸葛丽丽 |
| 争青小子 |
| 梅超风 |
| Tom |
| Tabm |
+----------+
默认是去重复的
mysql> select name from go1 union all select stuname from stu; # all不去重复记录
+----------+
| name |
+----------+
| 李白 |
| 张秋丽 |
| 张秋丽 |
| 李文才 |
| 李斯文 |
| 欧阳俊雄 |
| 诸葛丽丽 |
| 争青小子 |
| 梅超风 |
| Tom |
| Tabm |
+----------+
union的注意事项
1、 union两边的select语句的字段个数必须一致
2、 union两边的select语句的字段名可以不一致,最终按第一个select语句的字段名。
3、 union两边的select语句中的数据类型可以不一致。